Oral cancer is a serious health concern, but with early detection and the right care, it can be managed effectively. In this blog, we’ll discuss how to prevent oral cancer by avoiding key risk factors, spotting early symptoms, and maintaining good oral hygiene. We’ll also cover the treatment options available—from conventional methods to supportive care like homeopathy. Whether you’re looking to stay informed or support a loved one, this guide offers helpful tips in easy-to-understand language.
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer is a serious condition where abnormal cells grow in the tissues of the mouth or throat. It can develop in areas like the lips, gums, tongue, or inner cheeks. Often caused by lifestyle factors such as tobacco use or excessive alcohol consumption, oral cancer requires early detection for effective treatment. Regular dental check-ups and awareness about oral cancer can play a vital role in maintaining oral health and preventing complications.
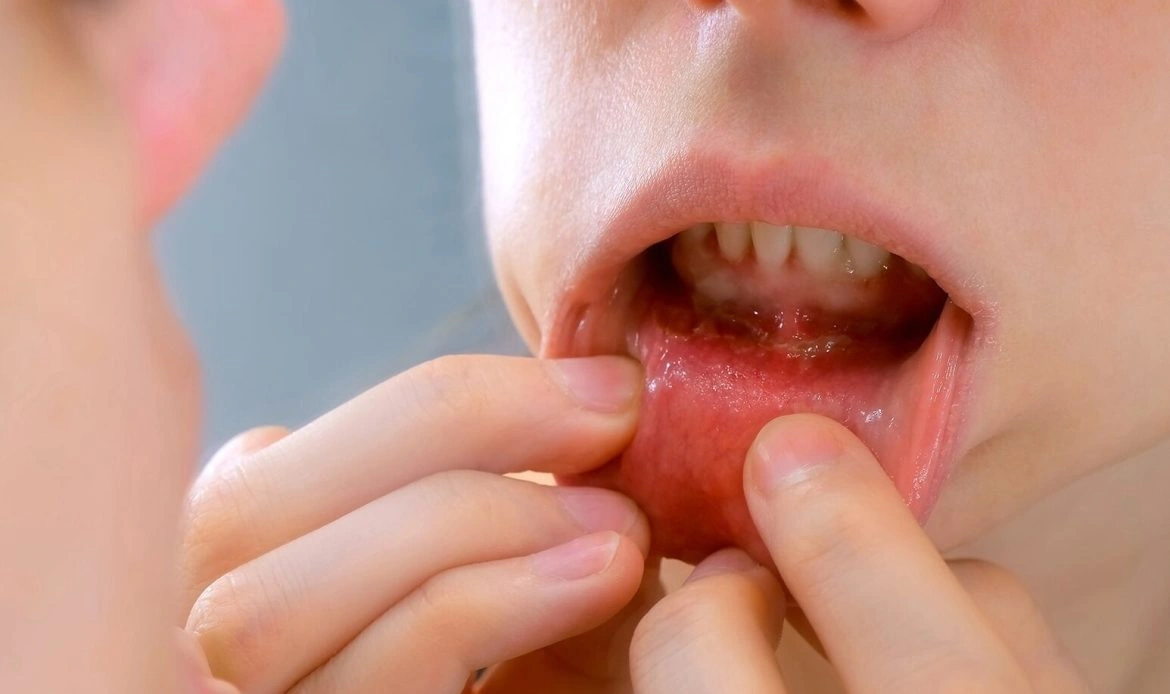
Oral Cancer Stages
Understanding oral cancer stages is crucial for effective treatment and recovery. Here’s a brief overview of how oral cancer and mouth cancer progress:
Stage 1: The tumor is small (less than 2 cm) and hasn’t spread to lymph nodes. Early detection of oral cancer stages at this level offers the best treatment outcomes.
Stage 2: The tumor grows between 2-4 cm but remains confined to the primary location, without lymph node involvement.
Stage 3: Cancer starts spreading to nearby lymph nodes, making treatment more complex. This is a critical stage for managing mouth cancer effectively.
Stage 4: The advanced stage where cancer spreads to distant organs or tissues, requiring comprehensive treatment approaches like surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.
Knowing these oral cancer stages helps patients and doctors strategize better treatment options for a higher chance of recovery.
Oral Cancer Progresses Through Four Stages:
Stage 1: The cancer is small (less than 2 cm) and hasn’t spread to lymph nodes. It’s easier to treat and has a high chance of recovery if detected early.
Stage 2: The tumor is slightly larger (2–4 cm) but still limited to the original area. There’s still no spread to lymph nodes, and treatment is usually effective.
Stage 3: Cancer has grown and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. This stage needs more aggressive treatment and close monitoring.
Stage 4: This is the advanced stage. Cancer spreads to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, or distant organs. Treatment becomes more complex and may involve surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
Understanding the stage helps determine the treatment plan and recovery chances.
Oral Cancer Last-Stage Symptoms
In the final stage, oral cancer symptoms become severe and may include:
1.Persistent Pain:
Ongoing pain in the mouth, jaw, or throat that doesn’t go away.
2.Difficulty Swallowing or Speaking:
Trouble moving the jaw or tongue, making it hard to eat, talk, or swallow.
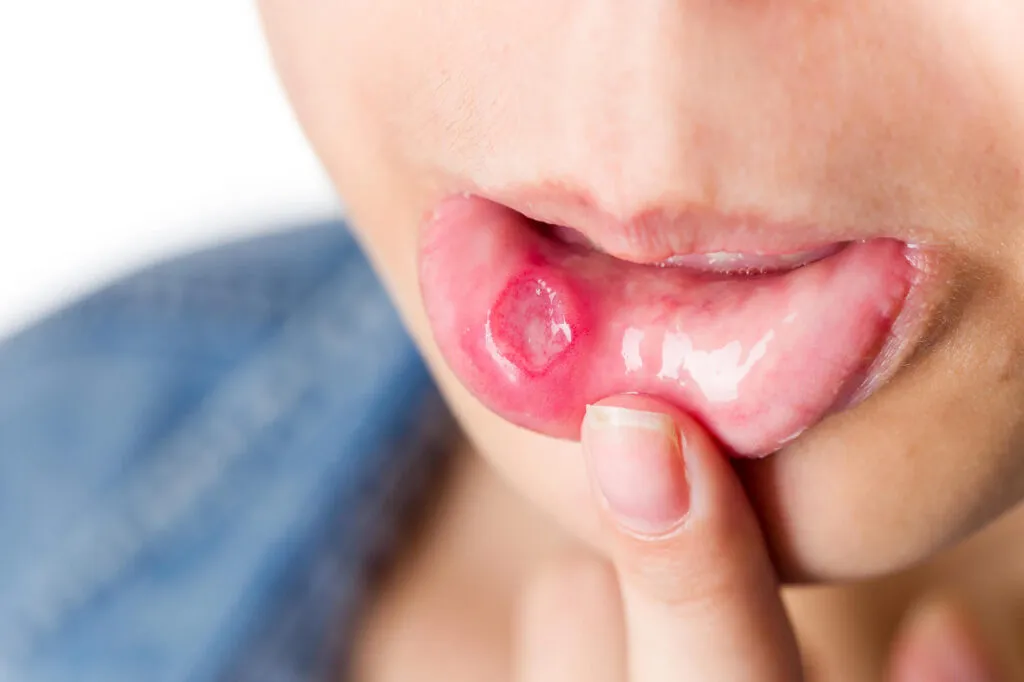
3.Large or Spreading Mouth Sores:
Non-healing ulcers that grow in size and may bleed easily.
4. Swelling or Lumps:
Visible swelling in the face or neck, often from enlarged lymph nodes.
5. Weight Loss and Fatigue:
Unexplained weight loss and constant tiredness due to the spread of cancer.
6.Bad Breath or Bleeding:
Persistent bad mouth odor and bleeding from gums or affected areas.
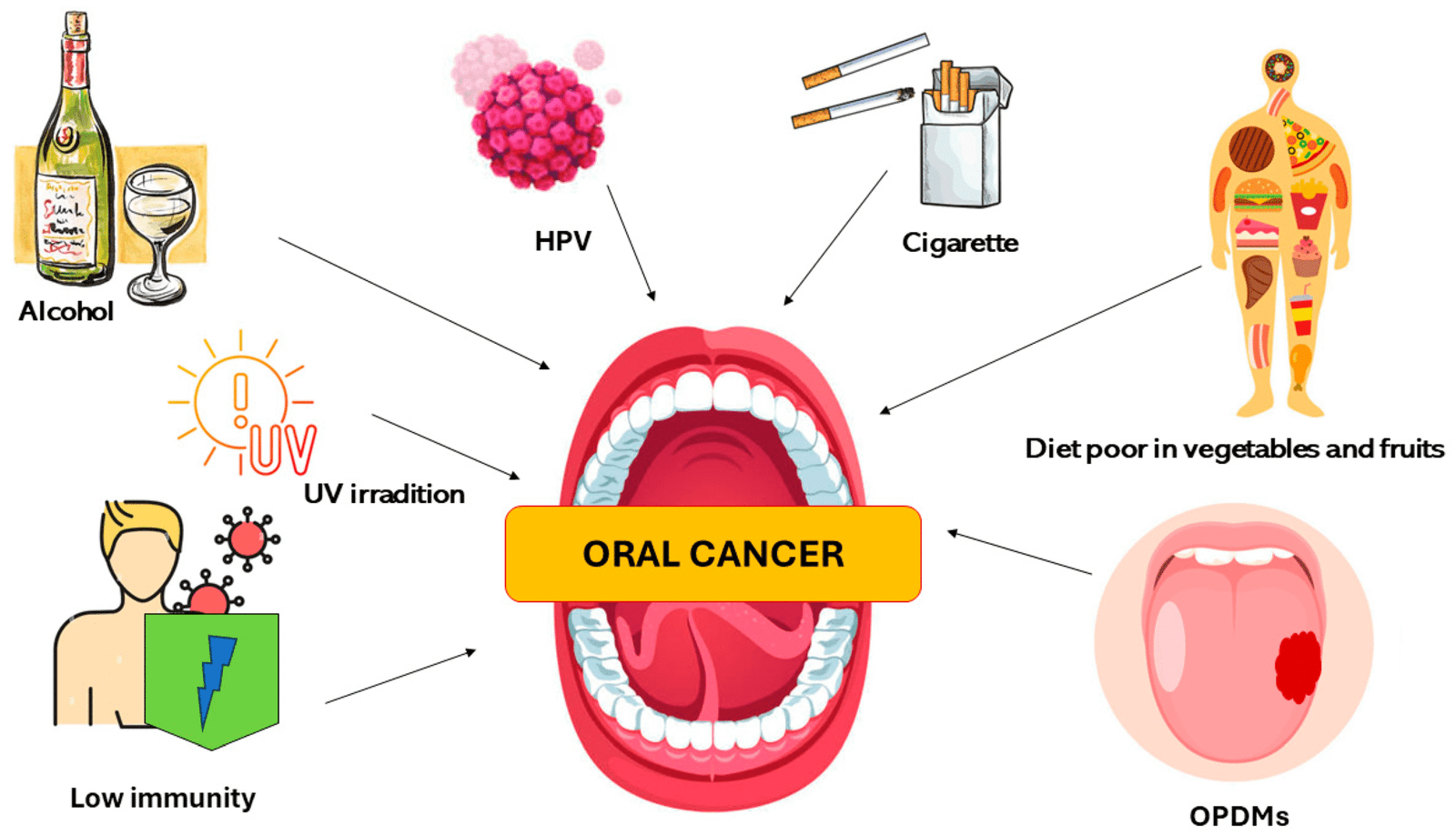
Causes of Oral Cancer
Key factors leading to oral cancer include:
1. Tobacco Use:
Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or chewing tobacco is one of the leading causes of oral cancer.
2.Alcohol Consumption:
Heavy or regular alcohol intake increases the risk, especially when combined with tobacco.
3. HPV Infection:
Certain types of human papillomavirus (especially HPV-16) are linked to mouth and throat cancers.
4. Poor Oral Hygiene:
Chronic irritation from sharp teeth, poor-fitting dentures, or poor oral care can contribute to cancer risk.
5. Poor Oral Hygiene:
Chronic irritation from sharp teeth, poor-fitting dentures, or poor oral care can contribute to cancer risk.
6.Sun Exposure:
Excessive sun exposure can lead to cancer on the lips, especially in people who work outdoors.
7.Family History:
A family history of cancer may increase your chances of developing oral cancer.
Prevention of Oral Cancer
You can lower your risk of oral cancer by:
1. Avoid Tobacco & Smoking:
Quit cigarettes, cigars, and chewing tobacco to reduce your risk significantly.
2. Limit Alcohol Intake:
Reduce or avoid heavy drinking, especially when combined with tobacco use.
3. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene:
Brush and floss daily, and visit your dentist regularly for checkups.
4. Use Lip Protection:
Apply lip balm with SPF and limit sun exposure to prevent lip cancer.
5. Eat a Healthy Diet:
Include fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins and antioxidants to support immune health.
6. Get Vaccinated for HPV:
HPV vaccines can lower the risk of virus-related oral cancers.
7. Regular Dental Checkups:
Dentists can spot early signs of oral cancer—early detection is key.
Simple lifestyle changes and early detection are key to preventing oral cancer and maintaining overall health.
Mouth Cancer Treatment with Homeopathy
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing mouth cancer by focusing on strengthening the body’s natural healing abilities. With remedies tailored to individual needs, it helps alleviate symptoms and supports overall well-being. The Homeopathic Treatment for Mouth Cancer aims to address pain, inflammation, and discomfort while enhancing immunity, making it a gentle and non-invasive alternative to conventional therapies.
In Conclusion
Oral cancer is a serious condition that requires awareness, timely diagnosis, and proper care. Understanding its stages, causes, and preventive measures can help reduce the risk and encourage early detection. Homeopathy offers a natural and supportive approach to managing mouth cancer by focusing on overall well-being and symptom relief. Stay proactive, prioritize regular check-ups, and maintain a healthy lifestyle to safeguard against oral cancer.