Liver cancer is becoming increasingly common, especially in regions with high rates of hepatitis infections and liver-related diseases. Unfortunately, many people remain unaware of its early signs, which leads to delayed diagnosis and limited treatment options. In this blog, Dr. Ankur Prakash, an experienced homeopathy practitioner, explains everything you need to know about liver cancer—from its types and symptoms to early warning signs and alternative treatment support through homeopathy, including insights into homeopathy treatment for fatty liver, which is often a precursor to more serious liver conditions.
What is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the liver begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a malignant tumor. The liver is an essential organ that performs over 500 vital functions, including:
- Filtering toxins from the blood
- Aiding digestion by producing bile
- Storing essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals
- Regulating blood sugar and cholesterol levels
When cancer develops in this organ, it compromises many of these critical functions, leading to serious health consequences.
Liver cancer is classified as either:
- Primary liver cancer – cancer that starts in the liver itself.
- Secondary (metastatic) liver cancer – cancer that spreads to the liver from other parts of the body, such as the colon, stomach, or lungs.
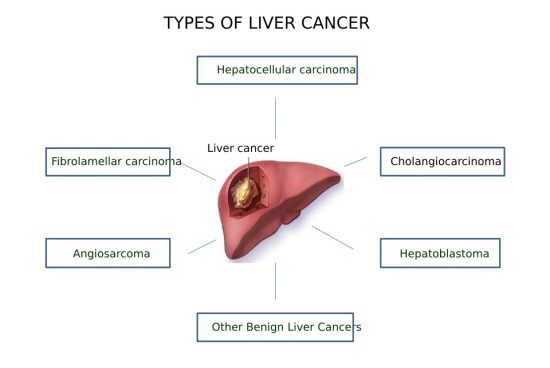
Types of Liver Cancer
Understanding the different types of liver cancer helps determine the most appropriate treatment:
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC):
- The most common type of primary liver cancer.
- Arises from hepatocytes, the main functional cells of the liver.
- Usually linked to chronic liver diseases like hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- The most common type of primary liver cancer.
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer):
- Originates in the bile ducts inside the liver.
- Less common but often more aggressive.
- Originates in the bile ducts inside the liver.
- Hepatoblastoma:
- A rare liver cancer seen mostly in young children.
- Has a high survival rate if detected early and treated promptly.
- A rare liver cancer seen mostly in young children.
- Angiosarcoma and Hemangiosarcoma:
- Rare cancers that start in the liver’s blood vessels.
- Usually aggressive and difficult to treat.
- Rare cancers that start in the liver’s blood vessels.
Each type behaves differently, affecting symptoms, treatment response, and survival rates.
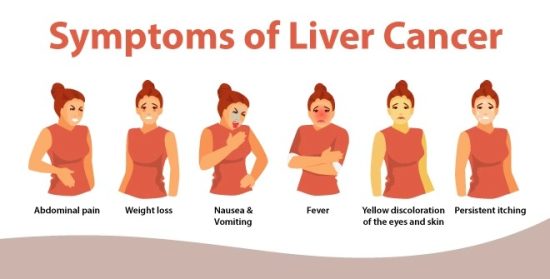
First Signs of Liver Cancer
The early signs of liver cancer are often vague and non-specific, which means they can easily be mistaken for symptoms of other less serious conditions, such as indigestion, fatigue, or viral infections. This makes early detection challenging. However, being aware of these subtle changes in the body is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
Recognizing these signs early can significantly improve the chances of successful management and treatment outcomes. Below are the most common early warning signs of liver cancer explained in greater detail:
1. Persistent Fatigue or Weakness
One of the earliest symptoms people experience is constant fatigue, even after getting proper rest. This can be due to the liver’s decreasing ability to filter toxins and maintain energy balance in the body. The fatigue is not just physical but also mental, affecting concentration and motivation.
2. Loss of Appetite and Unintended Weight Loss
Patients may start losing weight without changing their diet or exercise routine. This often occurs alongside a decreased appetite. The body, affected by the growing tumor and liver dysfunction, may begin to metabolize muscle and fat tissue, resulting in sudden and unexplained weight loss.
3. Right Upper Abdominal Pain or Discomfort
The liver is located in the upper right part of the abdomen. As liver cancer develops, the organ may become enlarged, causing a dull or sharp pain in that region. Patients may feel a sense of pressure or fullness, especially after eating small meals. This pain may also radiate to the right shoulder blade or back in some cases.
4. Jaundice (Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes)
One of the more noticeable signs, jaundice occurs when the liver is unable to properly process bilirubin, a yellow pigment in bile. As a result, bilirubin builds up in the blood, causing yellowing of the skin, the whites of the eyes, and sometimes dark urine. Jaundice is a strong indicator of liver dysfunction and should never be ignored.
5. Abdominal Swelling (Ascites)
Fluid buildup in the abdomen, known as ascites, is another early sign. This occurs when liver damage affects its ability to produce and regulate proteins and blood flow, leading to fluid leakage into the abdominal cavity. The swelling may be accompanied by discomfort, bloating, and shortness of breath.
6. Itchy Skin and Pale or Chalky Stools
Liver cancer can obstruct bile ducts, reducing the flow of bile and causing an accumulation of bile salts in the skin. This results in persistent itching, particularly on the palms, soles, or entire body. Additionally, the lack of bile in the digestive system can lead to pale, clay-colored stools—another sign of bile flow obstruction.
7. Low-Grade Fever, Nausea, and Vomiting
Many patients in the early stages report experiencing mild fevers that don’t resolve over time. This can be due to inflammation caused by the cancer. Nausea, bloating, and occasional vomiting may also occur due to the liver’s compromised function in digestion and detoxification.
8. General Feeling of Discomfort or Ill Health
Some individuals may not report specific symptoms but describe a general sense of being unwell. This may include mood changes, mental fog, irritability, or unexplained anxiety. These subtle changes are sometimes early warning signals that something more serious may be developing internally.
The Significance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of liver cancer can be life-saving. When detected in its early stages, treatment options are more effective and varied, including surgical resection, liver transplant, or localized therapies like radiofrequency ablation.
Benefits of early diagnosis:
- Increases eligibility for curative surgery or transplant
- Prevents further liver damage or metastasis
- Allows for integration of complementary treatments (like homeopathy)
- Improves long-term survival rates and quality of life
Diagnostic tools include:
- Liver function tests
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) blood test
- Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI of the liver
- Liver biopsy for confirmation
People at higher risk (such as those with hepatitis B/C or cirrhosis) should undergo regular screening.
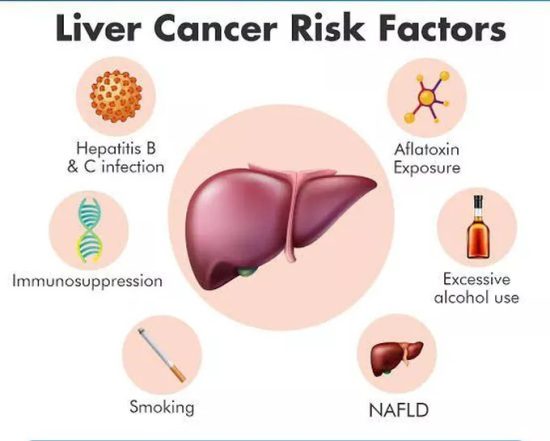
Risk Factors of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer rarely develops without underlying causes. Several risk factors contribute to the development of this disease by damaging liver cells, causing chronic inflammation, or triggering genetic changes that lead to cancerous growth. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for prevention, early detection, and management.
Several factors increase the risk of liver cancer by causing long-term liver damage or triggering abnormal cell growth:
- Chronic Viral Hepatitis (B or C):
Persistent infection with hepatitis B or C viruses causes ongoing liver inflammation. Over time, this leads to scarring (cirrhosis) and increases the risk of liver cancer. - Cirrhosis:
Cirrhosis is severe scarring of the liver from long-term injury due to hepatitis, alcohol, or fatty liver disease. It disrupts normal liver function and creates an environment prone to cancer development. - Alcohol Abuse:
Heavy, prolonged alcohol use damages liver cells and causes inflammation. This repeated injury can progress to cirrhosis and significantly raise the chance of liver cancer. - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
NAFLD results from fat accumulation in the liver, often linked to obesity and diabetes. Chronic liver inflammation from NAFLD can eventually lead to cirrhosis and cancer. - Exposure to Aflatoxins:
Aflatoxins are toxins produced by molds on improperly stored foods like nuts and grains. Long-term exposure causes genetic mutations in liver cells, increasing cancer risk, especially in certain regions. - Family History and Genetic Conditions:
Inherited liver diseases like hemochromatosis or a family history of liver cancer raise an individual’s susceptibility. Genetic factors can affect how the liver repairs and regenerates. - Smoking and Poor Diet:
Smoking introduces harmful carcinogens that can damage liver cells. A diet low in antioxidants and high in processed foods may contribute to liver inflammation and cancer risk.
Homeopathy Treatment for Liver Cancer
Modern homeopathy offers a supportive and integrative approach to liver cancer management. While not a replacement for mainstream cancer therapies, it plays an important complementary role.
Benefits of Homeopathy in Liver Cancer:
- Strengthens the immune system to better cope with the disease
- Alleviates the physical and emotional side effects of chemotherapy and radiation
- Supports liver function and reduces inflammation
- Improves sleep, appetite, and energy levels
- Addresses the patient’s overall mental, emotional, and physical state
At Dr. Ankur Prakash’s clinic, a personalized homeopathic treatment plan is developed for each liver cancer patient. This involves:
- In-depth case analysis
- Constitutional remedy selection
- Ongoing monitoring and adjustments
With a focus on natural healing, homeopathy can enhance the patient’s comfort and quality of life throughout their cancer journey.
Final Thought
Liver cancer is a serious but potentially manageable condition—if caught early. The first signs are often subtle, but staying alert to symptoms like fatigue, weight loss, or abdominal pain can lead to timely medical care.
If you’re at risk or notice any early warning signs, consult your doctor immediately. Integrating conventional treatments with homeopathy under expert guidance, such as from Dr. Ankur Prakash, can provide a more holistic and less distressing treatment experience.
Your health is your greatest asset—listen to your body, take action early, and choose care that heals both body and mind.