What Is Neurofibromatosis?
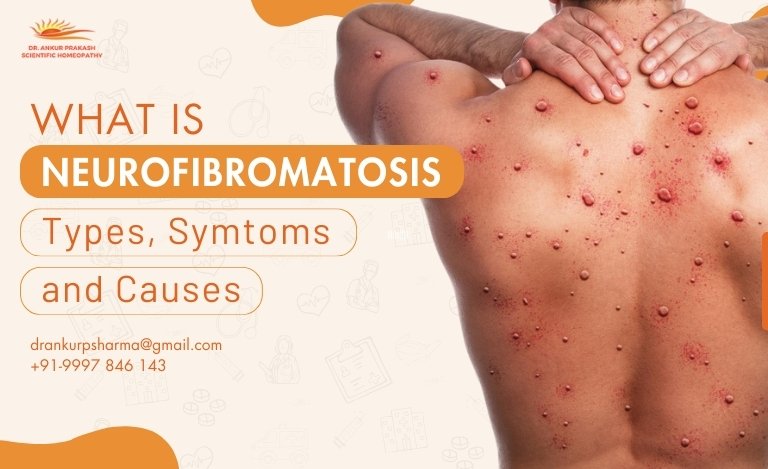
Neurofibromatosis (NF) is a genetic disorder that affects the growth and development of nerve cells, causing tumors called neurofibromas to grow on nerves in any part of the body. Most of these tumors are benign but can cause problems, such as pain and neurological problems, or, rarely, may become malignant. In general, NF is a condition present throughout an individual’s lifetime and can vary greatly in its intensity, from mild manifestations to significant morbidity problems.
Von Recklinghausen disease is a rather rare condition, but it is one of the most common inherited conditions that affect the central nervous system. It is caused by mutations in specific genes, but in some cases, there is no family history, making it sporadic. Along with neurological symptoms, individuals with NF often seek skin treatment due to the appearance of neurofibromas on the skin, which can cause both physical discomfort and cosmetic concerns. NF does not discriminate and can affect individuals of any race, gender, or ethnicity.
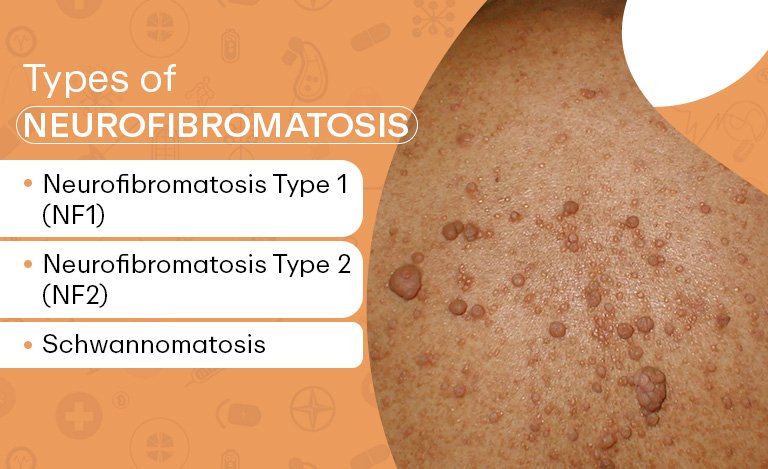
Types of Neurofibromatosis
There are three types of neurofibromatosis, which are very different from each other:
1. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1): The most common NF1, accounting for nearly 90% of the cases, results from mutations in the NF1 gene located on chromosome 17. It leads to reduced levels of neurofibromin, a protein that regulates cell growth, and thereby prevents it from proliferation, culminating in tumor formation. NF1 usually appears in childhood, and most patients are diagnosed by age 10. Common symptoms include café-au-lait spots (flat, light-brown skin patches), freckling in unusual areas such as the armpits or groin, Lisch nodules (small lumps on the iris), neurofibromas (soft, benign skin tumors), learning disabilities, and skeletal issues such as scoliosis or leg curvature.
2. Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2): Much rarer than NF1, NF2 results from mutations in the NF2 gene on chromosome 22, which encodes a protein called merlin or schwannomin that plays a role in cell growth regulation. Symptoms typically present in late teens or early adulthood. The classic feature of NF2 is bilateral vestibular schwannomas—benign tumors on the vestibulocochlear nerve, affecting hearing and balance. This may result in hearing loss, tinnitus, or a problem with balance. Other complications include meningiomas around the brain and spinal cord, as well as early-onset cataracts.
3. Schwannomatosis: The rarest form is schwannomatosis; this is caused by mutations in the SMARCB1 or LZTR1 genes. Symptoms typically appear in adulthood and include severe chronic pain, weakness, or numbness of muscles based on schwannomas—tumors that develop on the nerve sheaths. Schwannomatosis does not include cases of NF2 vestibular schwannomas or hearing loss.
Symptoms of Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis symptoms vary depending on the type but generally affect the skin, nerves, and other body functions. Here’s a brief overview:
1. NF1 Symptoms
Skin Marks: These are a common feature, which are light-brown spots, and freckles in the armpits or groin, which can appear during early childhood.
Tumors: Neurofibromas are soft, benign lumps that develop under the skin or along nerves, which may increase in size or number over time.
Bone Issues: Skeletal deformities such as bowing of the legs or spinal curvature (scoliosis) are often observed in individuals with NF1.
Learning Delays: Many children with NF1 have speech, learning, or attention problems, but the severity varies.
Eye Problems: Optic gliomas are tumors on the optic nerve that can affect vision and may need to be monitored for complications.
2. NF2 Symptoms
Hearing Loss: This can occur suddenly or gradually and is often bilateral because of tumors on the auditory nerves.
Ear Problems: Ringing in the ears (tinnitus) is another classic symptom of NF2.
Loss of Balance: Tumors damage nerves, leading to dizziness or loss of balance.
Neurological Problems: Weakness, numbness, or even facial paralysis can result from nerve-damaging tumors.
3. Schwannomatosis
Persistent Pain: There is severe and chronic nerve pain, which hampers one’s ability to live a normal life.
Numbness: The limbs of the patient are tingling or have reduced sensation.
Muscle Weakness: This weakness of the muscles may hinder normal physical activity.
Each type of neurofibromatosis has its own symptoms, and so problems occur early that should be dealt with.
Causes of Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis is normally due to certain mutations in genes regulating growth. The result of such mutation is the growth of uncontrolled cells. This will, most of the time, cause tumour development. These are some summary causes of NFs.
NF1: The mutated NF1 gene lacks instructions for neurofibromin production. Neurofibromin itself is a type of tumour suppressor; in its absence, cells grow pathologically and end up in tumors.
NF2: Mutations in the NF2 gene, which encodes the protein merlin. Loss of merlin function disrupts cell growth regulation, causing tumors to form on nerves.
Schwannomatosis: Mutations in the SMARCB1 or LZTR1 genes, which are also involved in cell growth regulation.
In about half of the cases, NF is inherited from a parent who also has the condition. The other half are caused by spontaneous genetic mutations that occur during conception.
What Are the Risk Factors for Neurofibromatosis?
The primary risk factor for von recklinghausen disease is having a parent with the condition. It is an autosomal dominant disorder, which means that if one parent has the condition, a child has a 50% chance of inheriting the mutation. Other risk factors include:
1. Family History: A strong family history of von recklinghausen disease strongly increases the risk of developing the condition.
2. Spontaneous Mutation: Even if there is no family history, a spontaneous mutation in the NF1, NF2, or any other related gene can cause NF.
Care of a Child With Neurofibromatosis
Care for a child with von recklinghausen disease is compassionate and proactive in handling the physical, emotional, and social challenges posed by the condition. Here are some main points in care:
1. Maintenance of Regular Medical Check-Ups
Monitoring routine is best performed by a group of specialists which consist of neurologists, dermatologists, geneticists, and orthopedic experts to try and detect complications at the earliest possible stage.
2. Educational Support
Most of the children diagnosed with NF1 will suffer from varying levels of learning disabilities or development delay. Teacher and school staff support for an individualized educational plan can facilitate success in school.
3. Emotional Support
It is emotionally draining to stay with a chronic condition at such an early age. The child can reveal his feelings to the counselor or support group.
4. Management of Symptoms
Managing neurofibromatosis symptoms involves targeted care for each type. For NF1, café-au-lait spots and neurofibromas should be monitored, with removal considered if they cause pain or cosmetic concerns. In NF2, hearing loss is managed with hearing aids or cochlear implants, while physical therapy helps address balance issues. For schwannomatosis, effective pain management, particularly in children, is crucial to improving quality of life. Regular follow-ups and personalized care are essential across all types.
5.Healthy Lifestyle
Help encourage a well-balanced diet, regular exercise, and ample sleep time for all-around wellness and health.
6. Genetic Counseling
Additionally, genetic counseling for NF patients is also available where the disease would be further explained and risk assessment on how it may likely be passed down to the next generations and which could further increase options in family planning.
7. Networking Support
Organizations with such groups like the Children’s Tumor Foundation or a local NF support group could give value-related resources, information, and connectivity among other families in this journey.
Consult us for Better Health
Dr. Ankur Prakash is recognized as one of the best homeopathy doctors in India, renowned for his specialized treatment in kidney disorders, thyroid issues, skin problems, and even cancer. With a compassionate approach, Dr. Prakash prioritizes his patients’ well-being by focusing on the root cause of health concerns.